Your trusted source for simple, practical nutrition advice and tips for a healthier lifestyle.
Spinach is a rich source of iron, providing about 2.7 mg per 100 grams. This leafy green is a valuable addition to a balanced diet.
Spinach, a nutrient-dense leafy green, offers numerous health benefits. Besides its high iron content, it is also packed with vitamins A, C, and K, as well as folate, magnesium, and antioxidants. These nutrients support overall health, boost the immune system, and enhance energy levels.
Consuming spinach regularly can help prevent anemia, improve eye health, and reduce oxidative stress. Easy to incorporate into various dishes, spinach can be enjoyed in salads, smoothies, soups, and more. Its versatility and nutritional profile make it an excellent choice for those seeking to improve their diet and well-being.

Credit: www.nutritiontactics.com
Introduction To Spinach
Spinach is a leafy green vegetable known for its rich iron content. This superfood is packed with essential nutrients, making it a staple in many diets. Below, we delve into its history and nutritional profile.
Brief History
Spinach has a long and fascinating history. Originating in ancient Persia, it spread to China in the 7th century. By the 12th century, it had reached Europe. Over the centuries, it became a beloved vegetable worldwide.
Nutritional Profile
Spinach is a powerhouse of nutrients. It’s low in calories but high in vitamins and minerals.
| Nutrient | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
| Iron | 2.7 mg |
| Vitamin A | 469 µg |
| Vitamin C | 28.1 mg |
| Calcium | 99 mg |
| Magnesium | 79 mg |
Spinach is also rich in antioxidants and fiber. It promotes overall health and boosts immunity.
Iron In Spinach
Spinach is a leafy green vegetable rich in iron. Eating spinach helps boost your iron levels. Iron is essential for making red blood cells. It also helps carry oxygen throughout your body. Including spinach in your diet is a great way to get this important mineral.
Iron Types
Iron in food comes in two types: heme and non-heme iron. Spinach contains non-heme iron. Non-heme iron is found in plant-based foods. It is different from heme iron, which is found in animal products.
Bioavailability
Bioavailability refers to how well your body absorbs iron. Non-heme iron in spinach has lower bioavailability. This means your body absorbs less of it. To enhance absorption, eat spinach with vitamin C-rich foods.
- Oranges
- Strawberries
- Bell peppers
Combining spinach with these foods helps you absorb more iron.
| Food Item | Vitamin C Content |
|---|---|
| Orange (1 medium) | 70 mg |
| Strawberries (1 cup) | 89 mg |
| Bell Pepper (1 medium) | 152 mg |
Health Benefits Of Iron
Iron is an essential mineral for our bodies. It helps in many ways. Spinach is a great source of iron. Consuming spinach can bring many health benefits. Let’s explore some of these benefits.
Energy Levels
Iron plays a key role in producing energy. It helps in forming hemoglobin. Hemoglobin carries oxygen in our blood. Oxygen is crucial for energy production. Low iron levels can lead to fatigue. Eating spinach can help boost your iron intake. This can improve your energy levels.
Immune Support
Iron also supports our immune system. It helps white blood cells work better. White blood cells fight off infections. Having enough iron can make your immune system stronger. Spinach can be a tasty way to get more iron. This keeps your body ready to fight germs.
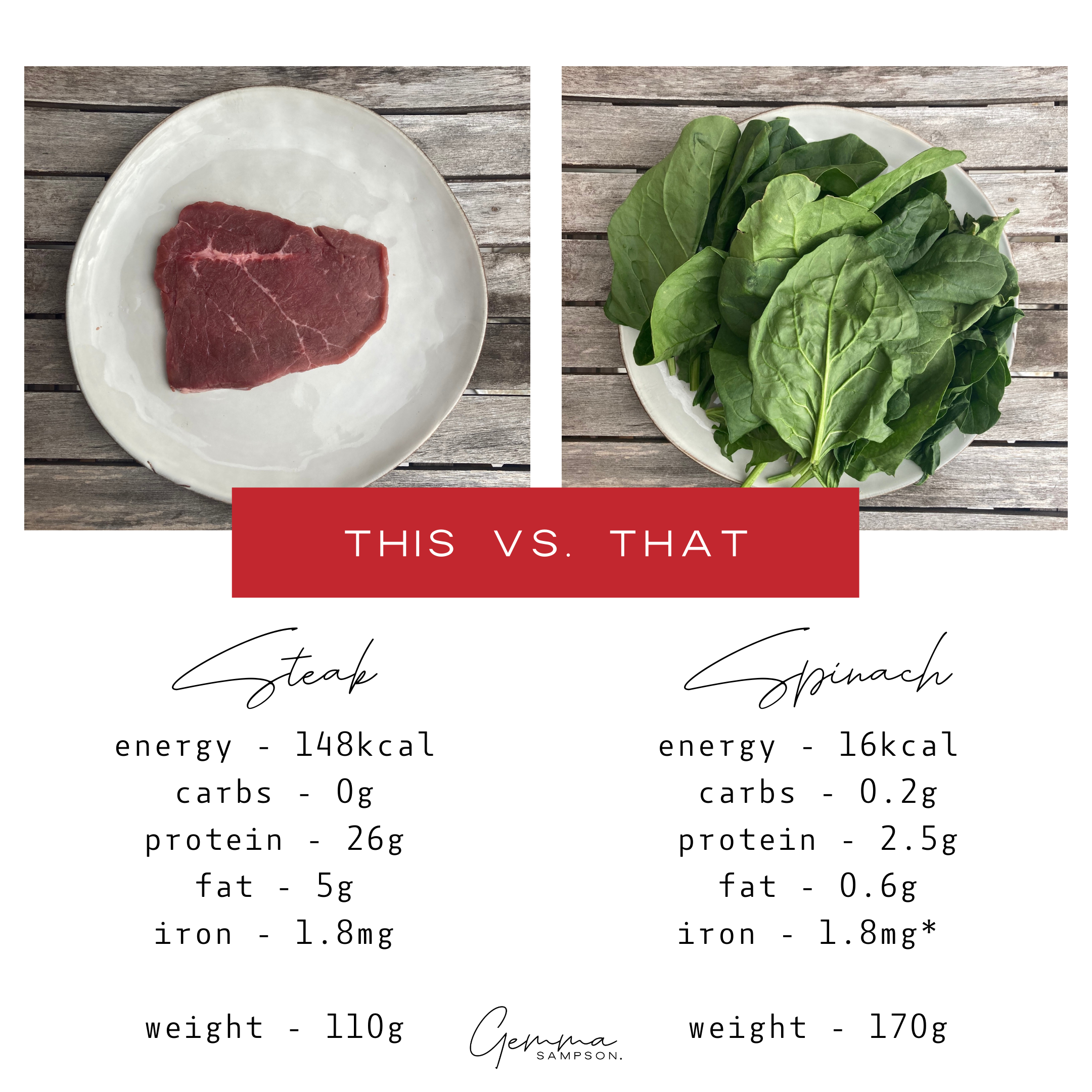
Credit: www.gemmasampson.com
Incorporating Spinach Into Diet
Spinach is a nutrient-dense green, rich in iron and vitamins. Adding spinach to your diet can improve health and energy levels. Let’s explore how to include this leafy green in your meals.
Raw Vs Cooked
Raw spinach retains more nutrients but has lower iron absorption. Cooked spinach increases iron absorption and reduces oxalates.
| Raw Spinach | Cooked Spinach |
|---|---|
| Retains more vitamins | Better iron absorption |
| Lower iron absorption | Reduces oxalates |
Both forms offer unique benefits. Mix both in your diet for maximum benefits.
Creative Recipes
Incorporate spinach into meals with creative recipes. Here are some ideas:
- Spinach Smoothie: Blend spinach with fruits and yogurt for a healthy drink.
- Spinach Salad: Combine raw spinach with nuts, cheese, and vinaigrette.
- Spinach Omelette: Add cooked spinach to your morning omelette.
Try these ideas to make your meals more exciting and nutritious.
- Spinach Pasta: Mix cooked spinach with pasta and sauce.
- Spinach Soup: Blend cooked spinach with broth and cream.
- Spinach Stir-Fry: Stir-fry spinach with garlic and soy sauce.
Experiment with these recipes to find your favorite ways to enjoy spinach.
Comparing Iron Sources
Iron is essential for our bodies to function properly. We need it to produce hemoglobin. Hemoglobin carries oxygen in the blood. But where can we get iron from? Let’s compare different sources of iron.
Plant-based Vs Animal-based
Iron comes in two forms: heme and non-heme. Plant-based foods contain non-heme iron. Animal-based foods contain heme iron. Heme iron is more easily absorbed by our bodies. But non-heme iron is still important.
Here is a comparison of common iron sources:
| Source | Iron Type | Iron Content (mg per 100g) |
|---|---|---|
| Spinach (cooked) | Non-Heme | 3.6 |
| Beef Liver | Heme | 6.5 |
| Chicken Breast | Heme | 1.0 |
| Tofu | Non-Heme | 5.4 |
Iron Supplements
Sometimes, food alone is not enough. Iron supplements can help meet iron needs. They come in many forms: pills, liquids, and even gummies. But be careful. Too much iron can be harmful. Always talk to a doctor before starting supplements.
Here are some common types of iron supplements:
- Ferrous sulfate
- Ferrous gluconate
- Ferrous fumarate
Each type has its pros and cons. Some are easier to digest. Others may cause fewer side effects. Choose wisely based on your needs and doctor’s advice.
Enhancing Iron Absorption
Spinach is rich in iron, but its absorption can be tricky. Enhancing iron absorption ensures you get the most from your spinach. Let’s explore effective ways to boost iron intake from spinach.
Vitamin C Pairing
Pairing spinach with foods high in Vitamin C can increase iron absorption. Vitamin C converts iron into a form more easily absorbed by the body.
- Citrus fruits like oranges and lemons
- Berries such as strawberries and blueberries
- Bell peppers
- Tomatoes
Try adding a squeeze of lemon juice to your spinach salad. This simple trick can significantly boost iron absorption.
Avoiding Inhibitors
Certain foods and drinks inhibit iron absorption. Knowing what to avoid can help you get the most iron from spinach.
| Inhibitor | Examples |
|---|---|
| Calcium-rich foods | Dairy products, fortified plant milks |
| Phytates | Whole grains, legumes |
| Polyphenols | Tea, coffee, red wine |
Avoid consuming dairy or coffee immediately after a spinach meal. This strategy helps to maximize iron absorption.
Potential Risks
While spinach is rich in iron, it also has some potential risks. Consuming spinach in excess or without proper balance can lead to some health issues.
Oxalates
Spinach contains high levels of oxalates. These compounds can bind with calcium in your body. This can form calcium oxalate, a component of kidney stones. People prone to kidney stones should monitor their spinach intake.
| Food Item | Oxalate Content (mg/100g) |
|---|---|
| Spinach | 750 |
| Beet Greens | 610 |
| Rhubarb | 500 |
Too many oxalates can also interfere with calcium absorption. This can lead to a calcium deficiency over time.
Overconsumption
Eating too much spinach can lead to nutrient imbalances. High amounts of iron can cause digestive issues like stomach cramps. Overconsumption can also lead to iron toxicity in extreme cases.
- Iron overload can cause nausea
- It may result in abdominal pain
- In severe cases, it can lead to organ damage
Balance is key to reaping spinach’s benefits without the risks. Aim for a varied diet to avoid overconsumption of any single nutrient.

Credit: www.compoundchem.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Iron Content In Spinach?
Spinach contains about 2. 7 mg of iron per 100 grams. It is a good source of non-heme iron.
How Does Cooking Affect Spinach’s Iron Content?
Cooking can reduce spinach’s iron content slightly. However, it also helps break down oxalates, making iron more absorbable.
Is Spinach A Good Source Of Iron For Vegetarians?
Yes, spinach is a great iron source for vegetarians. It provides non-heme iron, which is plant-based.
Can Spinach Improve Iron Deficiency?
Spinach can help improve iron levels if consumed regularly. Pair it with vitamin C-rich foods for better absorption.
Conclusion
Spinach is a powerhouse of iron, essential for your health. Including spinach in your diet can boost iron levels. Easy to incorporate into meals, it’s versatile and nutritious. Start enjoying the benefits of this leafy green today. Remember, a balanced diet is key for optimal health.





